Apache CXF - JAX-WS - Log Request/Response SOAP Messages Logback
Table of Contents
Apache CXF uses Java SE Logging for both client- and server-side logging of SOAP requests and responses. Logging is activated by use of separate in/out interceptors that can be attached to the requester and/or provider as required. These interceptors can be specified either programmatically (via Java code and/or annotations) or via the use of configuration files.
The following tutorial shows how to configure CXF logging interceptors using Logback for the contract first Hello World web service example from a previous post.
Tools used:
- CXF 3.0
- Spring 4.1
- Logback 1.1
- Jetty 8.1
- Maven 3.5
Specifying the interceptors via configuration files offers two benefits over programmatic configuration:
- Logging requirements can be altered without needing to recompile the code
- No Apache CXF-specific APIs need to be added to your code, which helps it remain interoperable with other JAX-WS compliant web service stacks
For this example Logback will be used which is a successor to the Log4j project. As a best practice the CXF java.util.logging calls will first be redirected to SLF4J (Simple Logging Facade for Java) as described on General CXF Logging. In other words a META-INF/cxf/org.apache.cxf.Logger file needs to be created on the classpath containing the following:
org.apache.cxf.common.logging.Slf4jLogger
As the Hello World example uses Spring, the commons-logging calls from the Spring framework will also be redirected to SLF4J using jcl-over-slf4j. Now that all logging calls of both CXF and Spring are redirected to SLF4J, Logback will receive them automatically as it natively implements SLF4J. The picture below illustrates the described approach.
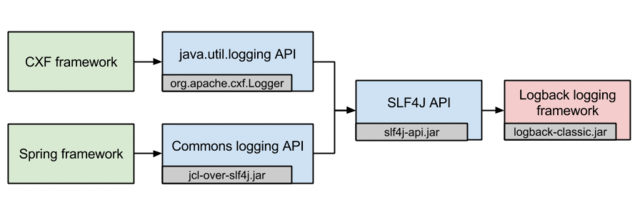
The below Maven POM file contains the needed dependencies for the SLF4 bridge jcl-over-slf4j and Logback logback-classic. In addition, it contains all other needed dependencies and plugins needed in order to run the example.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.codenotfound</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-jaxws-jetty-logging-logback</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<name>JAX-WS - CXF Log Request/Response SOAP Messages Logback</name>
<description>JAX-WS - CXF logging request and response SOAP messages using Log4j2</description>
<url>https://codenotfound.com/2014/09/jaxws-cxf-log-request-response-soap-messages-logback.html</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<slf4j.version>1.7.10</slf4j.version>
<logback.version>1.1.7</logback.version>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<cxf.version>3.0.3</cxf.version>
<spring.version>4.1.4.RELEASE</spring.version>
<maven-compiler-plugin.version>3.1</maven-compiler-plugin.version>
<jetty-maven-plugin.version>8.1.16.v20140903</jetty-maven-plugin.version>
<maven-failsafe-plugin.version>2.17</maven-failsafe-plugin.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jcl-over-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>${slf4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>${logback.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JUnit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- CXF -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-frontend-jaxws</artifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http</artifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<!-- Jetty is needed if you're are not using the CXFServlet -->
<artifactId>cxf-rt-transports-http-jetty</artifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven-compiler-plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<source>${java.version}</source>
<target>${java.version}</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- jetty-maven-plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mortbay.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${jetty-maven-plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<connectors>
<connector
implementation="org.eclipse.jetty.server.nio.SelectChannelConnector">
<port>9090</port>
</connector>
</connectors>
<stopPort>8005</stopPort>
<stopKey>STOP</stopKey>
<daemon>true</daemon>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>start-jetty</id>
<phase>pre-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>start</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>stop-jetty</id>
<phase>post-integration-test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>stop</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<!-- maven-failsafe-plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-failsafe-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${maven-failsafe-plugin.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>integration-test</goal>
<goal>verify</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<!-- cxf-codegen-plugin -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.cxf</groupId>
<artifactId>cxf-codegen-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${cxf.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>generate-sources</id>
<phase>generate-sources</phase>
<configuration>
<sourceRoot>${project.build.directory}/generated/cxf</sourceRoot>
<wsdlOptions>
<wsdlOption>
<wsdl>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/wsdl/helloworld.wsdl</wsdl>
<wsdlLocation>classpath:wsdl/helloworld.wsdl</wsdlLocation>
</wsdlOption>
</wsdlOptions>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>wsdl2java</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Logback Configuration #
Logback can be configured either programmatically or with a configuration script expressed in XML or Groovy format. For this example, a configuration script in XML is used as shown below. The script will write all logging events to a single file except for the request and response SOAP messages that will be written to a different file.
After defining some properties that contain the layout pattern and file names, two appenders are configured to write logging events to a rolling file. The first file jaxws-jetty-cxf-logging.log will contain all log events except for the ones emitted by the CXF logging interceptors as these are going to be written to jaxws-jetty-cxf-logging-ws.log.
The last section contains the different loggers and the level at which information is logged. The log level of the org.apache.cxf.services logger needs to be set to INFO in order to activate the SOAP logging events. In addition, the WS_LOG_FILE appender needs to be referenced in order to write the SOAP logging events to a different file.
Note the additivity="false" parameter which makes sure the log events are not written to appenders attached to its ancestors (in this case APP_LOG_FILE).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="60 seconds">
<!-- PROPERTIES -->
<property name="layout"
value="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level [%thread][%logger{0}] %m%n" />
<property name="logFile" value="jaxws-cxf-logging-logback" />
<property name="logFile-ws" value="jaxws-cxf-logging-logback-ws" />
<!-- APPENDERS -->
<appender name="APP_LOG_FILE"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<File>${logFile}.log</File>
<rollingPolicy
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${logFile}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
</fileNamePattern>
<maxHistory>30</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>${layout}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<appender name="WS_LOG_FILE"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>${logFile-ws}.log</file>
<rollingPolicy
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>${logFile-ws}.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
</fileNamePattern>
<maxHistory>30</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>${layout}</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- LOGGERS -->
<logger name="com.codenotfound.soap.http.cxf" level="INFO" />
<logger name="org.springframework" level="WARN" />
<logger name="org.apache.cxf" level="WARN" />
<!-- level INFO needed to log SOAP messages -->
<logger name="org.apache.cxf.services" level="INFO"
additivity="false">
<!-- specify a dedicated appender for the SOAP messages -->
<appender-ref ref="WS_LOG_FILE" />
</logger>
<root level="WARN">
<appender-ref ref="APP_LOG_FILE" />
</root>
</configuration>
The Requester (Client) #
In order to activate the logging interceptors provided by the CXF framework, there are two options. For the requester(client) the option where all logging interceptors are configured manually will be illustrated.
The other option, where the logging feature is used to configure all interceptors, will be shown in the provider section down below. Check the following link for more detailed information on the difference between CXF interceptors and features.
First, an instance of the abstract AbstractLoggingInterceptor class is created to enable pretty printing of the SOAP messages. Next, instances of the LoggingInInterceptor and LoggingOutInterceptor are specified which have as parent the previously defined abstractLoggingInterceptor instance. In a last step, the interceptors are added to the CXF bus, which is the backbone of the CXF architecture that manages the respective inbound and outbound message and fault interceptor chains for all client and server endpoints. The interceptors are added to both in/out and respective fault interceptor chains as shown below.
Note that interceptors can be added to a client, server or bus.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cxf="http://cxf.apache.org/core" xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/core http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/core.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<!-- allows for ${} replacement in a spring XML configuration from a
.properties file on the classpath -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:cxf.properties" />
<jaxws:client id="helloWorldRequesterBean"
serviceClass="com.codenotfound.services.helloworld.HelloWorldPortType"
address="${helloworld.address}">
</jaxws:client>
<!-- abstractLoggingInterceptor that will enable pretty printing of messages -->
<bean id="abstractLoggingInterceptor" abstract="true">
<property name="prettyLogging" value="true" />
</bean>
<!-- logging interceptors that will log all received/sent messages -->
<bean id="loggingInInterceptor" class="org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingInInterceptor"
parent="abstractLoggingInterceptor">
</bean>
<bean id="loggingOutInterceptor" class="org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingOutInterceptor"
parent="abstractLoggingInterceptor">
</bean>
<!-- add the logging interceptors to the CXF bus -->
<cxf:bus>
<cxf:inInterceptors>
<ref bean="loggingInInterceptor" />
</cxf:inInterceptors>
<cxf:inFaultInterceptors>
<ref bean="loggingInInterceptor" />
</cxf:inFaultInterceptors>
<cxf:outInterceptors>
<ref bean="loggingOutInterceptor" />
</cxf:outInterceptors>
<cxf:outFaultInterceptors>
<ref bean="loggingOutInterceptor" />
</cxf:outFaultInterceptors>
</cxf:bus>
</beans>
The Provider (Service) #
Activating the interceptors at provider(server) side will be done using the LoggingFeature that is supplied with the CXF framework.
First, an instance of the abstract LoggingFeature class is created with the prettyLogging set to true in order to enable pretty printing of the SOAP messages. As with the interceptors, the feature is added to the CXF bus in order to activate them as shown below.
Note that features can be added to a client, server or a bus.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:cxf="http://cxf.apache.org/core" xmlns:jaxws="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/core http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/core.xsd
http://cxf.apache.org/jaxws http://cxf.apache.org/schemas/jaxws.xsd">
<jaxws:endpoint id="helloWorldProviderBean"
implementor="com.codenotfound.soap.http.cxf.HelloWorldImpl"
address="/helloworld">
</jaxws:endpoint>
<!-- loggingFeature that will log all received/sent messages -->
<bean id="loggingFeature" class="org.apache.cxf.feature.LoggingFeature">
<property name="prettyLogging" value="true" />
</bean>
<!-- add the loggingFeature to the CXF bus -->
<cxf:bus>
<cxf:features>
<ref bean="loggingFeature" />
</cxf:features>
</cxf:bus>
</beans>
Testing #
Testing of the service is done using two unit and one integration test case. For the unit test cases, the requester and provider are created without Spring (using JaxWsServerFactoryBean and JaxWsProxyFactoryBean), as such the logging interceptor and feature need to be added programmatically as shown below.
package com.codenotfound.soap.http.cxf;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import org.apache.cxf.feature.LoggingFeature;
import org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingInInterceptor;
import org.apache.cxf.interceptor.LoggingOutInterceptor;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsProxyFactoryBean;
import org.apache.cxf.jaxws.JaxWsServerFactoryBean;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.codenotfound.services.helloworld.Greeting;
import com.codenotfound.services.helloworld.HelloWorldPortType;
import com.codenotfound.services.helloworld.Person;
public class HelloWorldImplTest {
private static String ENDPOINT_ADDRESS =
"http://localhost:9080/codenotfound/services/helloworld";
private static HelloWorldPortType helloWorldRequesterProxy;
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpBeforeClass() throws Exception {
createServerEndpoint();
helloWorldRequesterProxy = createClientProxy();
}
@Test
public void testSayHelloProxy() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setFirstName("Jane");
person.setLastName("Doe");
Greeting greeting = helloWorldRequesterProxy.sayHello(person);
assertEquals("Hello Jane Doe!", greeting.getText());
}
private static void createServerEndpoint() {
JaxWsServerFactoryBean jaxWsServerFactoryBean =
new JaxWsServerFactoryBean();
// create the loggingFeature
LoggingFeature loggingFeature = new LoggingFeature();
loggingFeature.setPrettyLogging(true);
// add the loggingFeature to print the received/sent messages
jaxWsServerFactoryBean.getFeatures().add(loggingFeature);
HelloWorldImpl implementor = new HelloWorldImpl();
jaxWsServerFactoryBean.setServiceBean(implementor);
jaxWsServerFactoryBean.setAddress(ENDPOINT_ADDRESS);
jaxWsServerFactoryBean.create();
}
private static HelloWorldPortType createClientProxy() {
JaxWsProxyFactoryBean jaxWsProxyFactoryBean =
new JaxWsProxyFactoryBean();
// create the loggingInInterceptor and loggingOutInterceptor
LoggingInInterceptor loggingInInterceptor =
new LoggingInInterceptor();
loggingInInterceptor.setPrettyLogging(true);
LoggingOutInterceptor loggingOutInterceptor =
new LoggingOutInterceptor();
loggingOutInterceptor.setPrettyLogging(true);
// add loggingInterceptor to print the received/sent messages
jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.getInInterceptors()
.add(loggingInInterceptor);
jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.getInFaultInterceptors()
.add(loggingInInterceptor);
jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.getOutInterceptors()
.add(loggingOutInterceptor);
jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.getOutFaultInterceptors()
.add(loggingOutInterceptor);
jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.setServiceClass(HelloWorldPortType.class);
jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.setAddress(ENDPOINT_ADDRESS);
return (HelloWorldPortType) jaxWsProxyFactoryBean.create();
}
}
Run the example by opening a command prompt and executing following Maven command:
mvn verify
The result should be that a number of log files are created in the project root directory. Amongst these files there should be jaxws-jetty-cxf-logging-ws.log and jaxws-jetty-cxf-logging-ws-test.log which contain the exchanged SOAP messages.
--------------------------------------
14:28:12.613 INFO [qtp846918683-20][HelloWorld_PortType] Inbound Message
----------------------------
ID: 2
Address: http://localhost:9080/codenotfound/services/helloworld
Encoding: UTF-8
Http-Method: POST
Content-Type: text/xml; charset=UTF-8
Headers: {Accept=[*/*], Cache-Control=[no-cache], connection=[keep-alive], Content-Length=[229], content-type=[text/xml; charset=UTF-8], Host=[localhost:9080], Pragma=[no-cache], SOAPAction=[""], User-Agent=[Apache CXF 3.0.3]}
Payload: <soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<person xmlns="http://codenotfound.com/services/helloworld">
<firstName>Jane</firstName>
<lastName>Doe</lastName>
</person>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
--------------------------------------
14:28:12.657 INFO [qtp846918683-20][HelloWorld_PortType] Outbound Message
---------------------------
ID: 2
Response-Code: 200
Encoding: UTF-8
Content-Type: text/xml
Headers: {}
Payload: <soap:Envelope xmlns:soap="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/">
<soap:Body>
<greeting xmlns="http://codenotfound.com/services/helloworld">
<text>Hello Jane Doe!</text>
</greeting>
</soap:Body>
</soap:Envelope>
This concludes our tutorial on setting up logging of the request and response SOAP messages using CXF and Logback. If you found this post helpful or have any questions or remarks, please leave a comment.